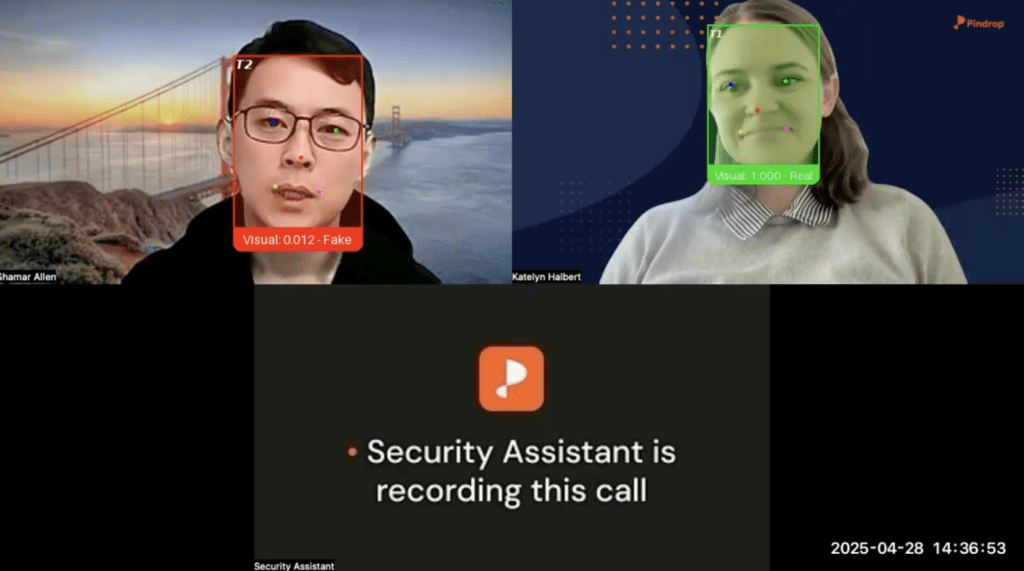
Deepfake Candidates Exploit Remote Hiring Loopholes
As IT services firms race to expand globally through remote hiring, a new and dangerous threat is emerging—AI-powered recruitment fraud. In one such scenario, an organisation was caught off guard when cybercriminals used deepfake video interviews and AI-generated resumes to bypass automated screening systems. Posing as legitimate employees, these imposters successfully cleared virtual interviews, joined project teams, and gained authorised access to internal and client systems. Within weeks, sensitive data was stolen and the fraudsters disappeared, leaving behind disrupted projects, financial losses, and severe reputational damage. In the era of deepfakes, hiring fraud is no longer just expensive—it can be catastrophic.
Impact and Risk Exposure
The fake employees were granted legitimate access to the company’s internal networks, client environments, software repositories, and confidential data. In a short span, intellectual property and sensitive project information were exfiltrated. Client deliverables were impacted, and multiple data breaches were traced back to the compromised accounts.
The incident exposed the organisation to significant legal, financial, and reputational risks. Breaches of client confidentiality clauses made the company liable under strict contractual obligations and regulatory frameworks such as the IT Act and data protection agreements. Loss of client trust could lead to suspension of ongoing projects, contract terminations, and long-term damage to the firm’s industry standing. The breach also attracted scrutiny from cybersecurity regulators, with potential consequences for future business opportunities.
Incident Response
Once warning signs emerged—such as inconsistent work quality and irregular communication patterns—the organisation initiated an internal investigation.
-
HR teams re-verified identity documents of all remote hires and engaged an external agency for independent background checks.
-
Cybersecurity teams traced access logs, disabled compromised accounts, and contained the breach.
-
Legal and compliance teams assessed client impact and regulatory exposure, initiating mandatory disclosures to affected customers.
-
Management ensured transparent communication with clients and internal stakeholders to manage fallout and restore confidence.
Remediation and Future Prevention
The root cause was an over-reliance on automated hiring processes with minimal real-time identity verification, creating gaps that fraudsters exploited. As part of remediation, access controls were tightened, client systems secured, and extended audits initiated to detect any further anomalies. Hiring and IT security policies were revised to embed stronger due diligence at the recruitment stage.
Additional preventive measures include:
-
Introducing live, proctored video interviews with facial liveness checks
-
Deploying deepfake detection tools in digital hiring workflows
-
Mandating third-party credential verification for all hires
-
Training HR and recruitment teams to identify fraud indicators
-
Closely monitoring new hires during probation, especially in remote roles
-
Including recruitment fraud scenarios in cybersecurity incident response plans
As AI continues to blur the line between real and fake identities, organisations must recognise that recruitment has become a frontline cybersecurity risk. Vigilance at the hiring stage is now essential to protecting systems, data, and trust.









